Enhydro Agate: A Comprehensive Guide to this Unique Gemstone
Share
Enhydro Agate: A Comprehensive Guide to this Unique Gemstone
Enhydro agate, a mesmerizing variety of agate, captivates with its stunning internal inclusions of water or other liquids trapped within its crystalline structure. This remarkable feature sets it apart, making it a highly sought-after gemstone among collectors, enthusiasts, and jewelry aficionados. This in-depth guide explores the fascinating world of enhydro agate, encompassing its formation, diverse properties, identification methods, historical significance, key localities worldwide, and its role in the gem and mineral trade. We will also delve into the scientific and gemmological aspects, providing a comprehensive understanding of this captivating gemstone. We will examine the various factors that contribute to the value and desirability of enhydro agates, as well as explore the ethical considerations surrounding their sourcing and trade.
Enhydro Agate Formation: A Journey Through Geological Time
The genesis of enhydro agate is a complex geological process spanning millions of years. It begins with the formation of cavities or vesicles within volcanic rocks, often during the cooling and solidification of lava. These cavities, sometimes referred to as geodes, provide the spaces necessary for the subsequent formation of agate. As silica-rich solutions seep into these cavities, they gradually deposit layers of microcrystalline quartz, a mineral known as chalcedony. This process creates the characteristic concentric banding patterns often seen in agates. The rhythmic deposition of these layers can result in stunning visual displays of contrasting colors and textures. During this deposition, water, gases, or other fluids become trapped within the growing agate structure, forming the hallmark liquid inclusions which give enhydro agates their unique appeal. The pressure and temperature conditions during formation play a crucial role in sealing these inclusions, preserving them for geological ages. The precise timing of fluid entrapment relative to the overall agate formation remains a subject of ongoing scientific inquiry.
The specific geological conditions that lead to the formation of enhydro agates are still being studied by geologists and mineralogists. Factors such as the chemical composition of the surrounding rocks, the rate of silica deposition, the presence of other minerals within the fluid inclusions, and the pressure and temperature fluctuations during formation all influence the size, shape, and composition of the resulting enhydro agate. The variations in these factors account for the wide diversity in color, banding patterns, and inclusion types observed in enhydro agates from different localities. The presence of additional mineral inclusions, beyond the water or gas bubbles, can further enhance the aesthetic appeal and value of the enhydro agate. These secondary inclusions can range from tiny crystals to more substantial mineral formations within the main cavity.
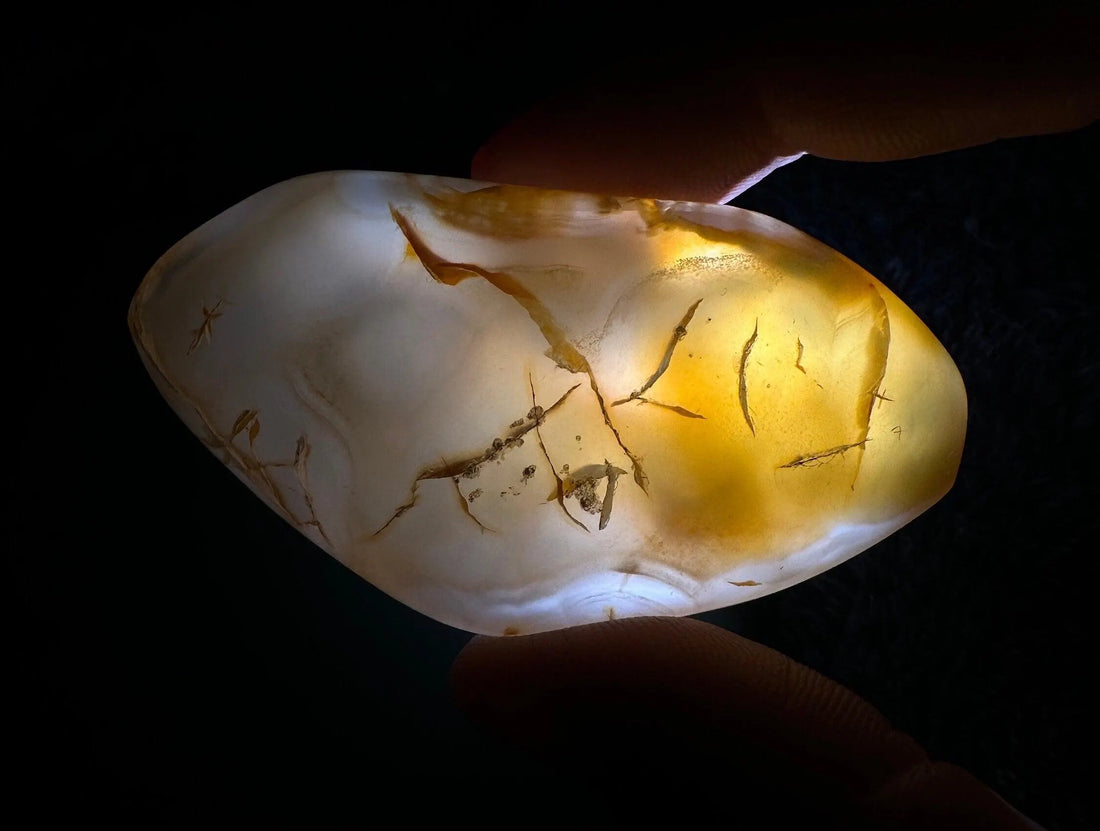
Enhydro Agate Properties: A Spectrum of Beauty and Durability
Enhydro agates showcase a captivating array of properties that contribute significantly to their aesthetic appeal and value. These properties make them desirable both for collectors and for use in jewelry. The interplay of these properties determines the overall quality and value of a particular specimen.
- Color: The color of enhydro agates is remarkably diverse, ranging from clear and translucent varieties to those exhibiting vibrant hues of white, gray, brown, yellow, red, green, and even blue. These colors are influenced by trace elements present during the agate's formation and the presence of different mineral impurities. The concentration and distribution of these impurities can create striking color zoning or banding within the agate.
- Transparency: Transparency varies considerably among different enhydro agate specimens. Some display exceptional clarity, allowing for easy visibility of the internal water bubbles, while others may be more opaque, partially obscuring the inclusions. The degree of transparency significantly influences the visual impact and perceived value of the stone.
- Internal Inclusions: The defining characteristic of enhydro agates is the presence of visible liquid-filled cavities. These inclusions vary dramatically in size, shape, and composition. They can contain pure water, gas bubbles, or even mixtures of both, along with microscopic mineral particles. The movement of these inclusions within the cavity is a captivating feature, making each enhydro agate a truly unique specimen. The size and clarity of these inclusions are key factors in determining the value of an enhydro agate.
- Hardness: Enhydro agate possesses a Mohs hardness of approximately 6.5 to 7, making it relatively durable for use in jewelry and other decorative applications. This durability, however, does not make it impervious to damage, and care should be taken to avoid impacts and scratches. Proper care and handling are crucial to preserve the integrity and beauty of enhydro agates over time.
- Luster: Enhydro agates typically exhibit a waxy to vitreous luster, adding to their overall aesthetic appeal. The luster contributes to the overall visual impact of the gemstone and influences its perceived quality.
- Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of enhydro agate varies slightly depending on the composition but generally falls within the range of 2.58 to 2.64. This property helps in distinguishing enhydro agates from other similar-looking gemstones.
Enhydro Agate Identification: Distinguishing Features and Expert Advice
Identifying enhydro agate requires a careful examination of its characteristics. While some visual cues can help, confirming a specimen as genuine enhydro agate frequently requires the expertise of a trained gemologist. Several factors are essential for accurate identification.
- Visible Inclusions: The most definitive characteristic is the clear presence of moving bubbles within the gemstone's internal cavity. Gently tilting or shaking the stone will reveal movement within the inclusion, providing conclusive evidence of its enhydro nature. The clarity and mobility of these bubbles are significant identification features.
- Banding Patterns: While not unique to enhydro agates, the characteristic concentric banding often found in agate can be a helpful visual clue. The pattern and color variations in the banding can enhance the visual appeal and value of the enhydro agate.
- Transparency and Clarity: The degree of transparency significantly influences the visibility of internal inclusions. High clarity is beneficial for showcasing the internal water or gas bubbles, while lower clarity may obscure or hinder the visibility of these key features.
- Gemological Testing: For definitive identification, especially when dealing with potentially valuable specimens, a qualified gemologist can employ various advanced techniques, including refractive index measurements, specific gravity testing, spectral analysis, and microscopic examination to confirm the identity and quality of the gemstone. These tests provide objective data to support the identification of enhydro agate and rule out potential imitations or similar-looking materials.
Enhydro Agate Localities: A Global Distribution of Geological Wonders
Enhydro agates are found in various locations around the globe, with some regions renowned for producing exceptional specimens. These localities reflect the diverse geological conditions that are conducive to the formation of this unique gemstone. The geological history and specific conditions of each locality impact the unique characteristics of the enhydro agates found there.
- United States: Several states, including Oregon, California, Arizona, and Washington, are known for producing various types of agate, including enhydro agates. The specific locations and geological formations within these states are often kept confidential by collectors and dealers to protect valuable resources.
- Brazil: Brazil is a significant source of many types of agates, including those with notable inclusions. The country's diverse geological formations provide ideal conditions for the formation of high-quality enhydro agates, often exhibiting vibrant colors and distinctive banding patterns.
- Uruguay: Uruguay also contributes a substantial number of beautiful agates, many of which exhibit exceptional color and banding patterns. Some of these agates also contain internal water or gas inclusions, showcasing the diversity of Uruguayan agate deposits. The quality and variety of Uruguayan enhydro agates have made them popular among collectors.
- Other Notable Localities: Enhydro agates have also been found in various locations across Africa, Europe, and Asia. These areas often produce specimens with unique characteristics related to the local geological formations, leading to a wide variety of colors, patterns, and inclusion types.
The specific locations of many enhydro agate discoveries are often kept confidential to protect these valuable resources and preserve the integrity of the locations themselves. This secrecy maintains the exclusivity of these exquisite gemstones, contributing to their allure and market value. Ethical sourcing and responsible collecting practices are crucial to ensure the long-term availability of enhydro agates.
Enhydro Agate Discovery and History: A Glimpse into the Past
While precisely dating the first discovery of enhydro agate is challenging, evidence suggests its appreciation dates back centuries. Ancient civilizations likely encountered and valued these unique stones for their aesthetic appeal and potential symbolic meaning. Further research into archaeological records may unveil more about its early use and cultural significance. The historical context of enhydro agate adds depth to our understanding of its cultural and economic impact throughout history.
The historical record concerning enhydro agate is fragmented, but existing information reveals its presence in various ancient cultures' jewelry and artifacts. These finds suggest a long history of human fascination with enhydro agate's unique properties. Specific examples of ancient use and cultural significance are still being researched and documented by archaeologists and historians. The scarcity of historical records underscores the need for further research into the early use and cultural significance of enhydro agates.
Enhydro Agate Scientific and Gemmological Information: Unraveling the Mysteries
Scientific and gemmological research plays a significant role in understanding and appreciating enhydro agates. This research contributes to both the scientific understanding of geological processes and the accurate identification and grading of these exceptional gemstones. The combination of scientific and gemmological approaches provides a holistic view of enhydro agates.
From a scientific perspective, studying the chemical composition of the trapped fluids within enhydro agates provides valuable insights into the ancient environment in which they formed. Analysis of these fluids can offer information on the temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions present during the agate's formation. This information contributes to a broader understanding of geological history and the processes that shaped our planet. The study of these fluids also sheds light on the conditions under which life may have emerged in ancient environments.
Gemmological studies focus on the optical properties, inclusion characteristics, and physical properties of enhydro agates. This research is essential for accurately identifying and grading specimens for the gem and jewelry trade. These studies contribute to the establishment of industry standards and best practices for evaluating the quality and value of enhydro agates. This research also helps to combat the trade in fraudulent or misrepresented gemstones.
Enhydro Agate Specifications and Value: Factors Influencing Desirability
The value of enhydro agate depends on a variety of factors, making each specimen unique and potentially valuable. Understanding these factors is crucial for both collectors and those involved in the gem and jewelry trade. The interplay of these factors determines the overall market value and desirability of each individual enhydro agate.
- Size and Weight: Larger, high-quality specimens are generally more valuable, as they are less common. Exceptional size and weight command premium prices in the market.
- Color and Pattern: Vivid and vibrant colors combined with intricate banding patterns increase desirability. Rare and unusual color combinations are highly valued.
- Clarity and Inclusion Quality: Well-defined, moving inclusions are highly prized, adding to the uniqueness of the stone. Large, clear, and mobile inclusions are considered more desirable.
- Overall Condition: The absence of fractures, chips, or other damage significantly affects value. Gemstones without any damage or imperfections are much more valuable.
- Rarity: The rarity of certain types of enhydro agates, based on their color, locality, and the size of the inclusions, can significantly affect their value. Unique and uncommon characteristics add to a specimen's desirability.
- Treatment: Enhydro agates are rarely treated, but any treatments, even minor ones, can negatively impact the value.
- Provenance and Documentation: A documented provenance, showing the origin and history of the gemstone, can increase its value and authenticity.
Ethical Sourcing and Responsible Collecting: Considerations for Enhydro Agate
The growing popularity of enhydro agates necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing and responsible collecting practices. It is crucial to support responsible mining and trading practices to ensure the sustainable availability of these gemstones for future generations. Supporting ethical sourcing ensures that the environmental and social impact of mining operations is minimized.
Consumers can actively contribute to ethical sourcing by:
- Purchasing from reputable dealers: Dealers committed to transparent and ethical sourcing practices provide valuable assurance of responsible acquisition.
- Inquiring about the origin of the gemstone: Asking about the provenance of the enhydro agate demonstrates a commitment to ethical sourcing.
- Supporting sustainable mining practices: Consumers can support initiatives that promote sustainable mining practices.
- Avoiding conflict minerals: It is imperative to avoid gemstones that originate from conflict zones.
Responsible collecting practices contribute to the long-term conservation of enhydro agate resources. These practices include respecting private land and obtaining necessary permits before collecting specimens.
Conclusion: The Enduring Allure of Enhydro Agate
Enhydro agate, with its captivating internal water bubbles, holds a unique and enduring place in the world of gemstones. Its formation, properties, and inherent beauty continue to captivate both scientists and collectors. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a thorough overview of this remarkable gemstone, deepening appreciation for its geological significance, aesthetic appeal, and the importance of ethical considerations surrounding its acquisition and trade. The enduring allure of enhydro agate stems from its unique combination of geological wonder and aesthetic beauty.